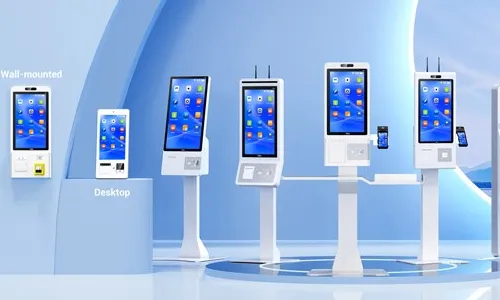
Self-service kiosks have become essential tools for businesses across retail, hospitality, healthcare, and transportation industries. They provide convenience, improve efficiency, and allow customers to complete transactions independently. The performance, durability, and usability of these kiosks depend heavily on the materials used in construction and the technology integrated into their design. Understanding these factors is crucial for businesses looking to invest in high-quality kiosks.
Materials Used in Self-Service Kiosk Manufacturing
A self-service kiosk is designed to withstand frequent use while maintaining a professional appearance. The materials chosen by a Self Service Kiosk Manufacturer determine the durability, aesthetics, and safety of the device.
Most kiosks are constructed with high-quality metals such as steel or aluminum for the frame and housing. Steel is often used for its strength and resistance to physical impact, making it ideal for high-traffic environments. Aluminum, while lighter, provides durability and is corrosion-resistant, which is beneficial for kiosks exposed to outdoor conditions. These metals are often powder-coated or treated to enhance durability and provide a clean, polished finish that is resistant to scratches and wear.
In addition to metals, self-service kiosks incorporate plastics and composite materials for panels, bezels, and ergonomic elements. High-impact plastics such as ABS or polycarbonate offer durability while reducing the overall weight of the kiosk. They are also resistant to heat, scratches, and impact, providing additional protection for internal components. For kiosks in outdoor environments, weather-resistant materials are used to withstand temperature fluctuations, humidity, and exposure to sunlight.
Glass is another critical material, primarily used for touchscreens. Most kiosks use tempered glass, which is highly resistant to breakage and scratching. Some advanced models include anti-glare coatings or chemical treatments to improve touch sensitivity, clarity, and visibility in bright environments. Capacitive or infrared touch technology is commonly integrated with these glass panels for accurate and responsive user interactions.
Technology Components in Modern Kiosks
The functionality of self-service kiosks depends on the advanced technology incorporated by manufacturers. These devices combine hardware, software, and networking systems to create a seamless and efficient user experience.
Processors and internal computing components are essential for ensuring smooth operation. Kiosks typically use energy-efficient CPUs with adequate memory and storage to handle multiple transactions simultaneously. Solid-state drives (SSD) are often preferred for their speed and reliability, reducing the risk of mechanical failures compared to traditional hard drives.
Display technology is another critical factor. Most modern kiosks use LCD or LED displays, providing high-resolution visuals for menus, forms, or advertisements. Touchscreen technology, including capacitive, resistive, or infrared systems, allows users to interact with the kiosk easily. Manufacturers optimize screen responsiveness and durability to ensure that kiosks can handle frequent use in busy environments.
Payment processing technology is integrated into many self-service kiosks, especially in retail and hospitality. Secure card readers, NFC-enabled terminals, QR code scanners, and contactless payment systems allow customers to complete transactions quickly and safely. These components are often designed to meet industry security standards, including PCI DSS compliance, to protect sensitive customer data.
Kiosks may also include printers, barcode scanners, and cameras for additional functionality. Receipt printers are designed for high-volume use, and thermal printing technology ensures quick, low-maintenance operation. Barcode scanners enable inventory tracking or ticket scanning, while cameras can be used for identity verification or interactive customer experiences.
Connectivity and Software Integration
Modern self-service kiosks rely on reliable connectivity to function effectively. Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks ensure that kiosks remain connected to central databases, cloud services, or payment gateways. Manufacturers integrate software platforms that manage transactions, inventory, analytics, and reporting, often providing remote monitoring capabilities.
Software customization allows businesses to tailor kiosks for specific tasks, such as self-checkout, ticketing, or customer feedback. User interfaces are designed to be intuitive and accessible, improving customer experience and reducing the need for staff assistance.
Durability and Maintenance Considerations
Combining high-quality materials with advanced technology ensures that self-service kiosks are durable and require minimal maintenance. Powder-coated metal frames, reinforced glass, and high-impact plastics protect internal components from wear, damage, or tampering. Energy-efficient components and reliable software also reduce downtime, ensuring that kiosks remain operational in demanding environments. Regular maintenance, software updates, and component inspections further extend the lifespan of the kiosks.
Conclusion
The materials and technology used in self-service kiosk manufacturing directly impact the performance, durability, and user experience of these devices. Metals like steel and aluminum provide structural strength, while high-impact plastics and tempered glass ensure durability and usability. Advanced computing components, touchscreens, payment systems, and connectivity solutions enable efficient, secure, and versatile operation. By understanding the materials and technologies involved, businesses can make informed decisions when investing in self-service kiosks, ensuring long-term value, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.