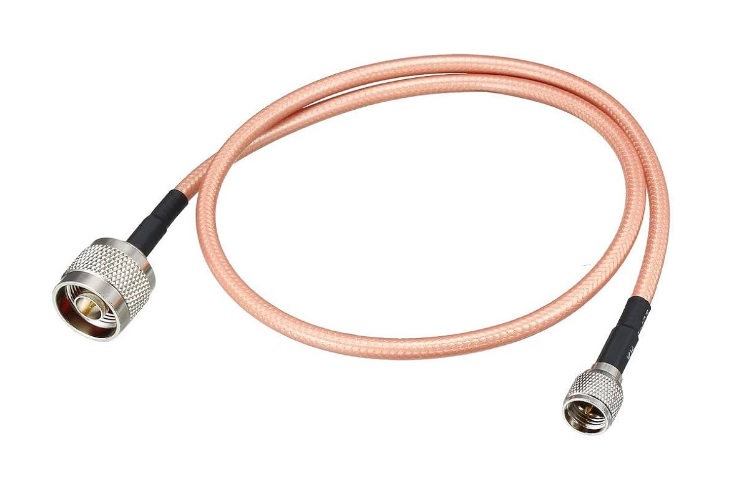
RF (radio frequency) cables are specialized cables designed to transmit radio frequency signals without significant signal loss or interference. Used in applications ranging from telecommunications and broadcasting to Wi-Fi and satellite communications, RF cables are fundamental to efficient and reliable data transmission. Selecting the right RF cable for a given application depends on factors such as frequency range, attenuation, and flexibility. RF cable manufacturers and RF cable suppliers offer various types of cables suited for specific use cases, ensuring optimal performance in diverse RF systems.
This article explores the purpose of RF cables, the different rf cable types available, and their applications across multiple industries.
Understanding RF Cables and Their Purpose
An RF cable is engineered to carry high-frequency signals while minimizing signal loss, interference, and noise. RF cables typically consist of a central conductor (often made of copper), an insulating layer, a shield (often braided or foil), and an outer insulation layer. This construction helps maintain signal integrity by protecting against external electromagnetic interference (EMI).
In RF systems, cables must handle signals with high frequency and bandwidth requirements. For instance, Wi-Fi, television antennas, and cellular networks all require specific RF cable types to ensure stable and clear signal transmission.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting an RF Cable
Choosing the appropriate RF cable depends on several critical factors:
- Frequency Range: The frequency range of an RF cable determines the maximum and minimum frequencies it can handle efficiently. Selecting an RF cable with a compatible frequency range for the application ensures optimal performance.
- Attenuation: Attenuation refers to the signal loss that occurs as the signal travels through the cable. Higher attenuation values result in greater signal loss, which can impact transmission quality, particularly over long distances.
- Impedance: Impedance matching between the cable and other components in the RF system is vital for reducing signal reflections and maximizing signal strength. Common impedance values for RF cables are 50 and 75 ohms, with each suited for different applications.
- Shielding and Interference Protection: Effective shielding protects RF cables from electromagnetic interference, helping to maintain signal clarity and quality. Depending on the application and surrounding environment, RF cables may have braided, foil, or even double-layer shielding.
Common Types of RF Cables
Several RF cable types are available, each designed to suit different applications, power requirements, and environmental conditions. Here are some of the most commonly used RF cables:
1. Coaxial Cable
Coaxial cables are widely used RF cables known for their durability, flexibility, and shielding capabilities. They consist of a central conductor, insulating dielectric, shielding, and an outer jacket. Coaxial cables are highly effective at transmitting high-frequency signals with minimal loss, making them ideal for applications in broadcasting, cable television, and Wi-Fi networks.
Coaxial cables come in different sizes and configurations, including RG-6, RG-11, and RG-58, each suited for specific frequency ranges and power requirements. For example, RG-6 cables are commonly used in television and internet connections, while RG-58 cables are ideal for shorter runs in communication systems.
2. Twinaxial Cable (Twinax)
Twinaxial cables are similar to coaxial cables but contain two inner conductors instead of one. Twinax cables are used for applications that require high-speed data transmission over short distances, such as data centers and storage networks. Twinax cables are less susceptible to interference, making them suitable for environments with multiple electronic devices operating at high frequencies.
3. Triaxial Cable
Triaxial cables are similar to coaxial cables but include an additional layer of shielding for extra interference protection. This structure enhances the cable’s ability to reject interference, making triaxial cables a good choice for applications that require high signal integrity, such as video transmission in broadcasting and scientific research environments.
4. Flexible and Semi-Rigid Cables
Flexible RF cables are designed for applications where cables need to bend and move, such as in portable devices and laboratory setups. These cables are easier to route through tight spaces and equipment. Semi-rigid cables, on the other hand, provide higher stability and lower attenuation but are more challenging to install due to their rigidity. They are often used in microwave and satellite communication systems, where stability and low signal loss are paramount.
5. Low-Loss Cables
Low-loss cables are designed to minimize signal attenuation, making them suitable for long-distance transmission. These cables are frequently used in high-power applications, such as cellular towers, satellite dishes, and broadcast stations. Low-loss cables often use premium materials and advanced insulation to achieve minimal signal degradation.
Applications of RF Cables Across Industries
RF cables are used in a variety of industries, each with its unique requirements for signal quality, frequency, and power handling. Below are some of the primary applications of RF cables:
1. Telecommunications
In the telecommunications industry, RF cables transmit signals between base stations, antennas, and receivers. High-frequency signals used in cellular communication systems require durable RF cables that can handle varying power levels while minimizing signal loss. High-power applications, such as 5G networks, often rely on specialized RF cables to handle large data volumes and provide stable connections.
2. Broadcasting and Media
In broadcasting, RF cables are used to transmit audio and video signals from one location to another. These cables are crucial for television, radio, and live event production. Coaxial cables, especially low-loss types, are commonly used in these applications to ensure clear signal transmission without interference.
3. Wireless Networks
RF cables are also essential in wireless networks, including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth systems. They are used to connect routers, antennas, and amplifiers, allowing for efficient signal transmission within a defined area. Flexible RF cables are often used in these setups for easy installation and reliable signal coverage.
4. Military and Aerospace
In military and aerospace applications, RF cables are essential for communication, navigation, and radar systems. These applications require cables that can withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as high altitudes, temperatures, and vibrations. High-power RF cables with robust shielding are typically selected for these applications to ensure reliable signal transmission in challenging environments.
5. Medical and Scientific Equipment
Medical imaging equipment, such as MRI and ultrasound machines, relies on RF cables to transmit signals for precise imaging. Additionally, RF cables are used in laboratory setups for scientific research, where maintaining signal integrity is essential for accurate measurements and data analysis.
Choosing Reliable RF Cable Manufacturers and Suppliers
Choosing reliable RF cable manufacturers and RF cable suppliers is essential for ensuring the quality and performance of RF systems. When selecting a manufacturer or supplier, consider the following factors:
- Quality Assurance: Look for manufacturers that adhere to industry standards, such as ISO certifications, ensuring the cables meet quality and performance benchmarks.
- Technical Expertise: Manufacturers with technical expertise in RF cable types and applications can provide valuable guidance in selecting the right cables.
- Custom Solutions: Some applications may require customized cables with specific lengths, shielding, or connectors. Reliable suppliers offer custom solutions to meet unique requirements.
- Reputation and Reviews: Choosing a supplier with a solid reputation and positive customer reviews can provide confidence in the cable’s performance and longevity.
- After-Sales Support: A manufacturer or supplier that offers robust after-sales support can provide technical assistance if issues arise during installation or operation.
Conclusion
RF cables play a vital role in transmitting high-frequency signals across industries, including telecommunications, broadcasting, military, and medical fields. With various RF cable types available, selecting the right cable for each application is essential for ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Coaxial, twinaxial, and triaxial cables each have unique benefits, from interference protection to flexibility.Partnering with reputable RF cable manufacturers and RF cable suppliers guarantees access to high-quality cables that meet industry standards and application requirements. By understanding the types, applications, and factors influencing RF cable selection, engineers and system designers can build reliable, efficient RF systems that deliver consistent performance