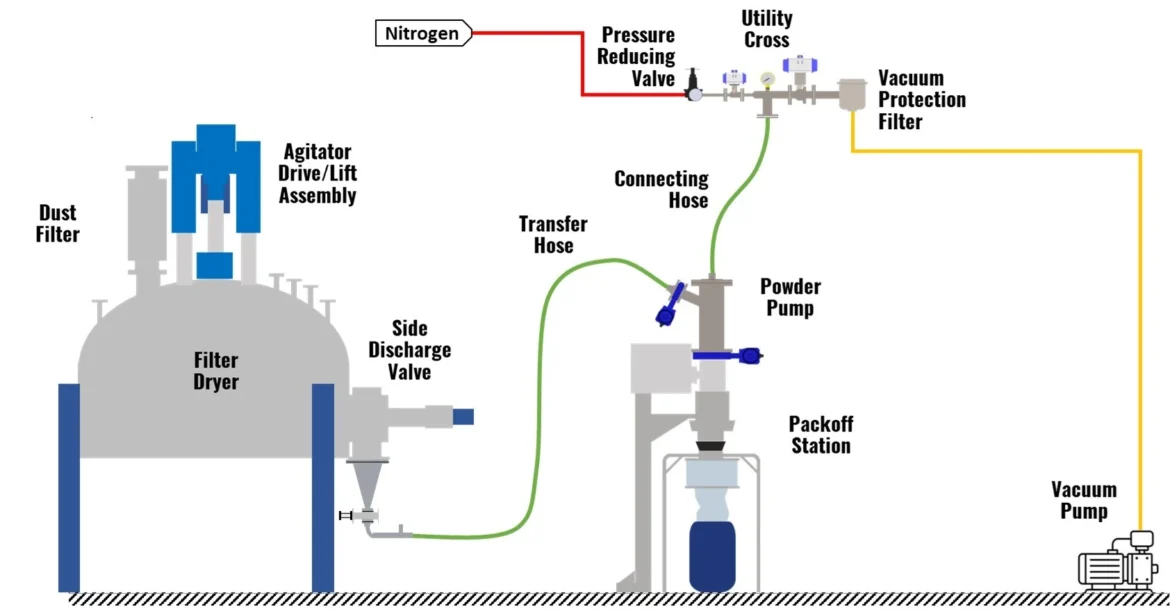
Agitated Nutsche Filters (ANFs) are essential in chemical, pharmaceutical, and fine chemical industries due to their ability to perform filtration, washing, and drying within a single enclosed vessel. The efficiency, durability, and safety of these systems are closely tied to the materials used in their construction. Proper material selection ensures chemical compatibility, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and compliance with regulatory standards. It is a critical factor in achieving reliable performance, consistent product quality, and long-term operational stability.
An Agitated Nutsche Filter typically consists of a vessel body, filter plate, mechanical agitator, heating and vacuum systems, and discharge mechanisms. Each of these components is exposed to varying chemical, thermal, and mechanical stresses, which makes careful selection of construction materials crucial. For industrial-grade applications and detailed specifications, you can explore this Agitated Nutsche Filter, widely recognized for its robust design and chemical resistance.
Vessel Body Materials
The vessel body forms the primary structure of the ANF and must withstand vacuum, slight pressure, and exposure to a wide range of chemicals. Stainless steel is the most commonly used material due to its excellent corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and ability to meet sanitary requirements. Specifically, stainless steel grades 304 and 316 are preferred for general chemical and pharmaceutical applications.
In processes involving highly corrosive or oxidizing chemicals, specialized alloys such as Hastelloy, titanium, or duplex stainless steel may be necessary. These materials provide enhanced resistance to aggressive substances, ensuring longevity and reducing the risk of contamination. Carbon steel can be considered in non-corrosive environments but often requires protective coatings or linings to prevent corrosion and ensure durability.
Filter Plate and Media
The filter plate supports the filtration medium and allows liquid to pass through while retaining solids. Filter plates are generally constructed from stainless steel due to their mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. In specific applications, high-strength alloys or coated metals are used to handle abrasive solids or chemically aggressive slurries.
Filter media selection is equally important. Options include woven stainless steel cloth, synthetic fabrics, or perforated metal plates, selected based on particle size, chemical compatibility, and process requirements. The media must resist wear, chemical attack, and repeated cleaning cycles while maintaining effective filtration performance. Proper material selection ensures consistent solids retention and prevents product contamination.
Agitator Materials
The agitator is a critical component for uniform mixing, preventing cake formation, and facilitating drying and discharge. Agitators are typically made from stainless steel to resist corrosion and maintain mechanical integrity under continuous operation.
For highly reactive or abrasive materials, corrosion-resistant alloys may be required. The agitator design—paddle, plough, or anchor—depends on the viscosity, particle size, and characteristics of the solids being processed. Using the correct materials for the agitator prevents contamination, ensures longevity, and maintains consistent performance over repeated cycles.
Seals and Gaskets
Seals and gaskets maintain the vacuum integrity of the vessel and prevent leaks. They must resist chemical attack, temperature fluctuations, and pressure variations. Common materials include PTFE, Viton, EPDM, and silicone, chosen based on the chemical nature of the processed materials and operational conditions. Proper selection of seals ensures vacuum efficiency, prevents leaks, and protects operators from exposure to hazardous substances.
Heating and Vacuum System Materials
Heating jackets and filter plates transfer thermal energy to the solids for drying, while the vacuum system accelerates liquid removal. Heating components are typically constructed from stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys to withstand temperature changes and chemical exposure. Vacuum lines, pumps, and fittings must also be made from compatible materials to prevent leaks, corrosion, and contamination. Ensuring durability of these components reduces maintenance requirements and increases the reliability of the process.
Discharge Mechanism Materials
Efficient discharge of solids is essential for reducing residue and minimizing product loss. Bottom valves, mechanical scrapers, or tilting vessels are commonly used for discharge. These components are generally made of stainless steel or corrosion-resistant alloys to handle mechanical stress and chemical exposure while ensuring smooth operation. Material selection in this area ensures longevity and safe handling of processed materials.
Regulatory Considerations
In pharmaceutical and food industries, ANF materials must comply with strict regulatory requirements. Stainless steel surfaces are often polished to reduce microbial growth and facilitate cleaning, meeting cGMP standards. All materials must also withstand cleaning, sterilization, and CIP (clean-in-place) procedures. Proper material selection ensures compliance, safety, and product quality.
Conclusion
Material selection is a critical factor in the performance, safety, and longevity of Agitated Nutsche Filters. Stainless steel is the most widely used material due to its corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and regulatory compliance, but specialized alloys may be necessary for highly corrosive, abrasive, or reactive processes. Careful selection of materials for the vessel body, filter plate, agitator, seals, heating system, and discharge mechanisms ensures reliable operation, reduces maintenance needs, and maintains consistent product quality. By considering chemical compatibility, mechanical requirements, and regulatory standards, manufacturers can optimize the efficiency and safety of Agitated Nutsche Filters in chemical and pharmaceutical production.