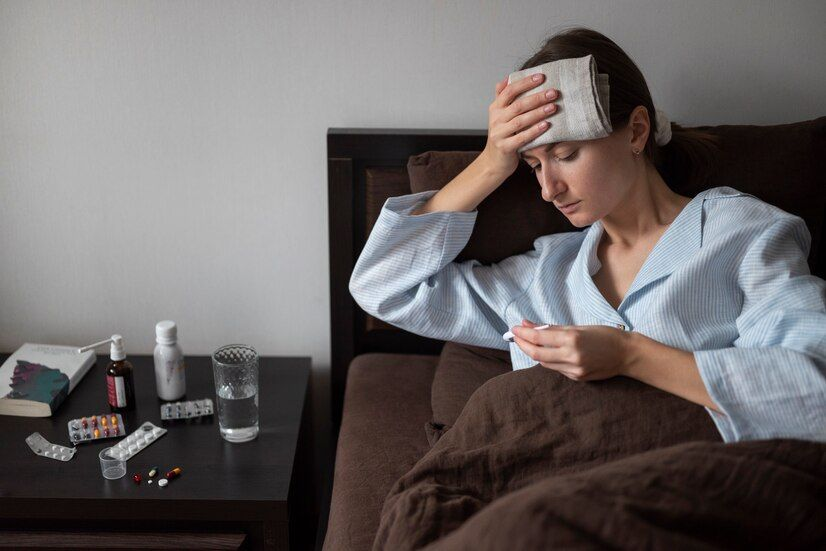
What Is a Viral Fever?
Viral fever is caused by infections with viruses, a type of microorganism that invades living cells to replicate. When the immune system responds to the infection, the body’s temperature increases, resulting in a fever. This is a natural defense mechanism to kill or inhibit the virus.
Viral fevers can be caused by a variety of viruses, such as:
- Influenza virus (flu)
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV)
- Dengue virus
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Adenovirus
The fever can vary in severity depending on the virus, the person’s health, and their immune response. It’s important to monitor the symptoms, as viral fevers share similar signs with other infections.
Common Viral Fever Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of viral fever helps with early intervention and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: The hallmark of viral fever is an elevated body temperature, often ranging between 100°F and 103°F. In some cases, the fever may fluctuate throughout the day, especially with viruses like dengue or chikungunya.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Viral fever often leads to feelings of extreme tiredness and weakness, even if you haven’t engaged in physical activity. This is a response to the body’s immune system working to fight the virus.
- Headache: Persistent headaches are a frequent symptom, often described as a dull or throbbing sensation.
- Body Aches: Muscle pain and joint stiffness are common, especially with fevers caused by influenza, dengue, or other similar viruses.
- Chills and Shivering: Even when experiencing a fever, you may feel cold or experience shivers, a common response to sudden body temperature changes.
- Sore Throat and Cough: Respiratory viruses often present symptoms like a sore throat, dry cough, or congestion.
- Runny Nose or Nasal Congestion: Especially with respiratory viruses, congestion and a runny nose can be early signs.
- Loss of Appetite: Many patients report a reduced appetite during the course of a viral fever.
Less Common Symptoms of Viral Fever
In addition to the more typical signs, viral fever may sometimes present other, less common symptoms, such as:
- Skin Rash: Certain viruses, such as dengue or measles, can cause rashes to appear on the skin along with fever.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Some individuals experience nausea or vomiting, especially when viral fever is linked to gastrointestinal infections.
- Diarrhea: Viral gastroenteritis can lead to diarrhea, along with stomach cramps and dehydration.
- Swollen Lymph Nodes: Viral infections may cause lymph nodes, particularly around the neck and under the jaw, to swell.
- Redness in Eyes: Eye redness or conjunctivitis is sometimes seen with viral infections, especially in the case of viral conjunctivitis or certain strains of adenovirus.
If you experience any severe or unusual symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical care, as certain viral fevers can lead to serious complications.
Causes of Viral Fever
Viral fever is caused by several types of viruses, which can spread through:
- Airborne Transmission: Viruses like the flu, common cold, and COVID-19 spread through droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
- Contaminated Surfaces: Viruses can survive on surfaces like doorknobs, phones, and countertops. Touching these surfaces and then your face can lead to infection.
- Mosquito Bites: Some viral fevers, such as dengue and chikungunya, are transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes.
- Direct Contact: Close contact with an infected person, such as shaking hands or sharing utensils, can facilitate the transmission of viruses.
Preventing viral fever often involves practicing good hygiene, including frequent handwashing, wearing masks, and avoiding contact with infected individuals.
Diagnosis of Viral Fever
To diagnose viral fever, your healthcare provider will begin by reviewing your symptoms and performing a physical examination. They may ask about your recent activities, travel history, and contact with infected individuals.
Diagnostic tests that may be used include:
- Blood tests: To detect the presence of viral infections and check for changes in white blood cell counts.
- Chest X-rays: In cases where respiratory symptoms are severe, to rule out pneumonia.
- Throat swabs: To identify specific viruses, like the flu or COVID-19.
Based on the test results, the doctor can determine the best course of treatment.
Treatment and Home Care for Viral Fever
There is no specific cure for viral fever since it is caused by viruses. However, treatment focuses on symptom relief and supporting the body’s immune response.
Common treatment options include:
- Rest: Ensure adequate rest to allow the body to fight the infection.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids like water, electrolyte solutions, or clear soups to stay hydrated.
- Antipyretics: Medications like acetaminophen (paracetamol) or ibuprofen can help reduce fever and body aches.
- Warm Baths: Taking a warm bath can help alleviate fever-related discomfort.
If symptoms worsen or persist, consult a doctor for further medical management.
Conclusion
Viral fever is a common but manageable condition. By understanding its symptoms and seeking appropriate care, you can effectively manage it and prevent complications. Always consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment to ensure a quick recovery.